Table of contents
- Cryptocurrency Explained
- Why Do We Need Cryptocurrency?
- Crypto VS Fiat
- How Does Cryptocurrency Work?
- How to Store and Use Cryptocurrency?
- Cryptocurrency Mining: where does crypto come from?
- Are Cryptocurrencies Legal?
- What are the Types of Cryptocurrency?
- Why Does Cryptocurrency Have Value?
- Summary
- Keep Exploring
This is a first post in a series of educational posts about cryptocurrencies and web3 space. Subscribe to my newsletter above to receive a notification about new releases in this series.
Why would anyone need to create a cryptocurrency? The answer remains open, partly due to the characteristics of cryptocurrency. Previously, there was no convenient and quick way to make anonymous digital payments with a high level of security. Since Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, was created, this isn't an issue anymore.
In a series of DeFi basics articles, me and you, dear future crypto punk, will finally connect the dots on what and why crypto, and discover a new wild west of financial freedom, crypto hacks, anonymous mumbo jumbo, and maybe a few conspiracy theories. This is another set of words put together to educate the uneducated on the essence of crypto, how to use it, how not to lose a house chasing fantasy profits, and how not to get rekt by:
cryptocurrency scams, such as sending your money to fake Elon Mask to get 2x back,
getting your funds locked and hijacked on exchanges,
exposing your crypto wallet secrets to thieves,
and many more in between.
Some of the info will be a little academic, some conspiratorial, but none will be intentionally misleading. I have a background in economics, marketing, business, and programming. Therefore, I hope this experience will allow me to use better sets of words to assist you in understanding why so many people, including me, invest in cryptocurrency and blockchain technology as a whole.
2009 is considered the official cryptocurrency year of birth when the Bitcoin network began its operation. Satoshi Nakamoto, a mythological character or group of people who are still unknown, is considered the creator of Bitcoin and other cryptographic currencies. The Bitcoin protocol was first published on Satoshi Nakamoto's behalf. Satoshi also initiated the first transaction in the genesis block.
Satoshi Nakamoto has many years of experience in cryptography and IT technologies, which was implemented into the Bitcoin infrastructure. The number of years of development and the research conducted has yet to be discovered precisely.
The term "cryptocurrency" was first used in a Forbes article about Bitcoin in 2011. Forbes readers and fans of the new virtual currency liked the name so much that it soon began to characterize the whole industry.
Cryptocurrency Explained
Cryptocurrency is a digital form of money based on cryptography technology. Cryptography is data encryption that does not have a physical appearance but exists only in digital form (distributed ledger). Its main features are anonymity, decentralization, and security.

Cryptocurrencies are circulated within the system directly (P2P/peer-to-peer) – without the participation of a third party. Each of the participants is equal. No one has privileges, regardless of their social or financial status. At the heart of this virtual money is a decentralized open database – blockchain. Blockchain is a distributed ledger allowing to send and receive transactions from one person to another.
Most cryptocurrencies have an emission limitation (the release of new coins into circulation). In the Bitcoin network, it is 21 million "coins." And in such cryptocurrency as Ethereum (ETH, ether), for example, there is no restriction on emission. Ethereum has a variable rate of emission and no supply cap.
Why Do We Need Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency can be helpful for various purposes, from shopping to saving money. Here are a few major uses for crypto as a finance tool:
Payments. And not just transactions but anonymous, fast, and direct transactions. They are carried out between private individuals and for purchasing goods and services on the Internet.
Money storage. It is almost impossible to "steal" crypto from a wallet. Since all operations are irreversible and use private keys, it is unrealistic to intercept or hack them. If you have not given your private key to anyone, your cryptocurrency will always be safe.
Investments. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are considered investment assets due to exchange rate fluctuations and an overall increase in popularity. Moreover, crypto is suitable for short-term earnings by trading on the exchange and long-term, as the exchange rate shows an upward trend.
Business. More and more companies and services are starting to accept payments in cryptocurrency transactions. Crypto startups that raise funds through ICOs (crowdfunding) have become everyday things. You can initiate fundraising through an ICO if you have a business idea related to blockchain or virtual currency.
Luckily, cryptocurrency is not the only use case of the blockchain. Looking at this technology separately from digital currency, the list of current and potential future use cases goes on and on.

Crypto VS Fiat
When the word "currency" is mentioned, images of banknotes and banks pop up in your mind. We are used to the fiat system in the financial sector, a standard, regulated currency such as a dollar or a euro. The main differences between cryptocurrencies and fiat currencies are:
Cryptocurrency has no physical appearance. Yes, fiat also exists in electronic form, but there are no banknotes and no cryptocurrency coins. Make sure to distinguish physical coins, storage wallets, and QR codes that work with crypto with actual physical currency.
Cryptocurrency is not issued by the central bank and is not tied to the economy of any country. No one controls the primary issue and the following emission of cryptocurrency. No one can influence these processes. The price is formed by supply and demand on the market. It is not directly connected with the economy of any country.
Cryptocurrency is anonymous. To work with a bank or payment system (Paypal, Venmo, etc.), you must specify at least part of your personal data. Cryptocurrency doesn't require anything, just like paper cash. Each member is anonymous. All information about the owner's wallet (account) is a set of characters in the wallet address (example of wallet address: 19emjx4vqHPn6ZTsh1ZNbBD7uFZqWA5Cq)

Bitcoin Wallet Address Example
- Direct transactions. This virtual currency system has no processing centers, intermediaries, issuers, and third parties. The transaction goes from Alice to Bob directly, like giving cash to someone physically. No one can suspend, recall, freeze, or cancel the transaction. All transactions are irreversible, so if you receive bitcoins in your wallet, you can be sure that no one can take them away.
How Does Cryptocurrency Work?
Most cryptocurrencies function and circulate on the blockchain. This is an open, decentralized database where information about all transactions is recorded and stored. It is not located on any separate computer, server, or hard drive, but is divided into nodes. It is supported by active members of the network – ordinary users of full-fledged wallets.
Individual cells with recorded data are blocks. Moreover, all the blocks are interconnected in the chain – from this comes the name Blockchain.

Blockchain Simplified Block Creation Process
The connection is established by writing the hash of all previous blocks to the new block. Because of this, it is almost impossible to change a separate block – you will have to "hack" all the blocks in the chain.
Hash is simply a result of all data included in the transaction/block encrypted into a single alphanumeric string. To illustrate, let's take a phone number +1-617-949-4546 and sum all numbers multiple times:
1+6+1+7+9+4+9+4+5+4+6 = 56
5+6 = 11
1+1 = 2 – this number is called hash sum or simply hash.
The prefix "crypto" is because Bitcoin and other currencies use encryption and cryptographic hash functions. So each member of the network has a private key and a public key. The private key is used to sign a "transfer of ownership." This is the basis of all transactions and ensures the transfer of cryptocurrency from one participant to another. And the public key is used to verify other people's transactions in the blockchain. In other words, a private key is a secret signature that lets the blockchain know that the transaction is legitimate, and a public key is the account number that you can share with anyone to receive money.
How to Store and Use Cryptocurrency?
To use Bitcoin or any other coin or token, you need a cryptocurrency wallet and buy/receive Bitcoin. The majority of beginners store their coins on the cryptocurrency exchanges where they purchased them. This is a risky storage method because centralized exchanges don't create a unique wallet for you. They make a record in their system saying that user johnstone@gmail.com bought 1 BTC, and they promise to deliver your Bitcoin upon request. If you decide to keep your "promised" bitcoin on such an exchange, you will lose it once the company files for bankruptcy or is hacked. This has happened multiple times since 2009 (e.g., MT.Gox exchange hack) because crypto exchanges are lucrative targets for hackers.
The safest way to store cryptocurrency is offline on a hardware wallet (also called a cold wallet) to protect yourself from hacking and theft of funds.
Ledger Nano S
Trezor One
The hardware wallets, Ledger Nano S and Trezor One are considered one of the safest. Both support more than 1000 cryptocurrencies and cost around $60. More expensive products from both companies are also available, so feel safe to shop for other models. The wallet is easy to set up, and you can immediately transfer the cryptocurrency purchased on the exchange. Make sure to buy wallets from the official store or reseller, and check the box upon arrival. I don't recommend buying it from Amazon or eBay due to the risk of receiving a wallet where your private key has been exposed. If your package is damaged or opened – never use such a wallet. It most likely was compromised on the way from the manufacturer to your home. Suppose the seller is official, and the box looks unopened. In that case, you can start using it as your safe cryptocurrency storage device.
Cryptocurrency Mining: where does crypto come from?
The most common method of cryptocurrency issue and emission is through mining. In Bitcoin, mining is solving cryptographic tasks of varying complexity using computing equipment capacities. There is also forging – a particular form of crypto mining with voting and initial cryptocurrency emission (ICO - Initial Coin Offerings).

Bitcoin Mining Illustration
Why is this necessary at all, and why do miners get rewards? This process is similar to how torrent trackers work. The participants of the tracker are engaged in the distribution of files. For this, they receive a rating, which is subsequently used to download new data. As peers in torrent trackers distribute files, miners are using computing power to maintain network performance.
The ultimate goal of mining is to reach a secure, tamper-resistant consensus by compilation of a digital signature (hash) that closes the block. As soon as the block completes, the miner receives a reward, and a new block begins to form. Different cryptocurrencies use different computing power, such as processors (CPU), video cards (GPU), or specialized equipment (ASIC, FPGA). Mining is one method of earning cryptocurrencies.
The following protocols (consensus algorithms) are used to determine the mining method:
Proof-of-Work (PoW). This is a security algorithm in which the authenticity of transactions is verified through the performance of specific tasks. In PoW, the higher the equipment performance, the more coins are mined.
Proof-of-Stake (PoS). This concept states that you can mine cryptocurrency or validate block transactions and receive a reward according to the number of coins you have stacked. PoS is a "credit" mining. The more coins are stacked, the greater the reward.
Proof-of-Activity (PoA). PoA is a hybrid option between PoS and PoW that attempts to bring the best of both.
Other less common protocols include Proof-of-Capacity, Proof-of-Burn, and Proof-of-Storage. By the time I finish writing this series, a few more will most likely be introduced.
The choice of equipment and its power depends on the hashing algorithm. Bitcoin has SHA-256. This algorithm is "tied" to equipment performance. Litecoin has Scrypt, a modified SHA-256, with great emphasis on RAM.
SHA-256 is a one-way function that converts a text of any length into a string of 256 bits. This is known as a hashing function. In this case, it is a cryptographically secure hashing function. The output of such a function tells you very little about the input.

Examples of mining equipment
How to Get or Buy Cryptocurrency
In addition to mining, there are many other, more straightforward ways to earn cryptocurrencies. Let's consider some of them:
Faucets. Faucets are services for distributing Bitcoin and other coins for performing small tasks: solving the captcha, web surfing, and so on.
Bounty. Bounty is the process of advertising new crypto projects through social media posting, reposting, document translations, and so on. Initially, you get tokens for free, which will soon become a full-fledged cryptocurrency.
Blogging/copywriting. Members of Steemit – a social network owned and operated by its users – receive a reward in the form of internal cryptocurrency when making a new post. Later, you can sell it on exchanges.
Bitcoin and alternative coins, or simply altcoins (Ethereum, Ripple, etc.), can also be easily purchased. This is done through cryptocurrency exchanges, BTMs (Bitcoin ATMs), or directly from other people. If you want to buy crypto online, it is enough to have a debit or credit card. However, most legit exchanges require proof of identity, so don't be surprised if you are asked to provide a picture of your ID. This is because of the regulations governments put in place to reduce the anonymity of crypto users. You can also buy crypto with your fiat money (cash) using machines installed in shopping malls, convenience stores, and gas stations. Usually, the price is 5-10% higher than you see on big exchanges, so this is a less popular option.
Are Cryptocurrencies Legal?
Cryptocurrencies are legal in most countries, although there may be restrictions on their use or exchange. For example, in 2021, the United States government proposed regulations on cryptocurrency transactions that could go into effect by 2022. Additionally, some countries have imposed taxes on cryptocurrency transactions or exchanges. Despite these regulations, cryptocurrencies remain a viable option for users who want to make secure and anonymous transactions without involving traditional banks or other financial institutions.
What are the Types of Cryptocurrency?
In general, cryptocurrencies are divided into two forms, coins and tokens. What is the difference between a "Coin" and a "Token"? A Coin is a cryptocurrency that can operate independently. A Token is an asset that depends on another cryptocurrency as a "hosting" platform. The most popular "token platform" is Ethereum, on which most tokens are based. Ethereum is the second largest cryptocurrency after Bitcoin and has the most currently known use cases (DeFi, NFTs, games, etc.), while Bitcoin is designed for financial transactions (DeFi) only.
Why Does Cryptocurrency Have Value?
How reasonable is cryptocurrency's price, and how is it supported? There are different opinions on this. In the summer of 2017, the American IT billionaire Mark Cuban criticized Bitcoin and the crypto as a whole on Twitter:
Anyone anywhere can buy a stock. #crypto is like gold. More religion than asset. Except of course gold makes nice jewelry. #crypto notsomuch t.co/xp334BCRa2
— Mark Cuban (@mcuban) June 6, 2017
After that, the rate declined, and Mark added:
You know it’s a bubble when a random twitter thread bounces the price. t.co/7gBGYU3JcQ
— Mark Cuban (@mcuban) June 6, 2017
However, later, Cuban began to invest in ICOs and even advised people to keep 1/10 of their funds in cryptocurrency. There are two main features for a "successful" currency to exist – a store of value and a medium of exchange. Besides, there are essential features such as scarcity, divisibility, utility, transportability, durability, and the ability to counterfeit it. In short, bitcoin meets all of the qualifications even better than fiat money. However, there is still an issue with cryptocurrency's status as a store of value. Like regular fiat currencies, most cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, are not backed by the economy, precious metals (gold, silver, etc.), or other commodities. The value of Bitcoin has been driven mostly by the speculative interest of market participants. Due to the relatively low evaluation (market capitalization) of cryptocurrencies compared to, for example, the stock market, it is easier to manipulate the price. Thus, artificially inflating or deflating the bubble. This is likely to decline as Bitcoin continues to see greater mainstream adoption and a constant increase in market capitalization, which makes it harder for a single manipulator to influence the price.
So what drives the cryptocurrency price?
Firstly, cryptocurrency mining requires powerful equipment that consumes a lot of electricity and gradually loses its performance. It turns out that depreciation is partially transferred to the value of the coins. Miners are the ones who bring newly mined coins onto the market. Since mining is quite an expensive process for every miner, they wouldn't want to sell their coins cheaper than they spent on mining. This creates a scarcity that also significantly influences the price. The reduced supply of coins with the same or rising level of demand pushes the price up.
Secondly, blockchain technology. Blockchain is something that no other payment system has. The blockchain is universal, reliable, and decentralized. At the same time, it guarantees anonymity and high transaction speeds. And it is used in various fields, from the financial sector to alternative energy. These are some obvious advantages that help determine the value of cryptocurrencies.
The market determines the value of these virtual coins. The greater the demand for a particular cryptocurrency, the higher its value. Demand, in turn, depends on the advantages that the coin offers. If tomorrow BTC is accepted as the official currency of China, for example, then its value will soar. Demand is heavily formed based on news, new developments, company announcements, and other factors.
There are also speculative leaps in the price – the so-called "pumps and dumps". They are provoked by large traders (manipulators) on exchanges seeking to make money out of thin air. They are not particularly interested in how much the coin costs. Having many assets, manipulators can have a short-term effect on the exchange.
Advantages and disadvantages of cryptocurrency
Let's summarize the crypto advantages we discussed so far and introduce some disadvantages to complete the picture.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Anonymity. No information about the wallet owner's identity, only the wallet address. | Due to the lack of regulation, wallets are not insured as bank accounts. |
| The open-source code of the algorithm allows everyone to participate in blockchain operations. | Governments can negatively influence the use and adoption of cryptocurrency by their country's residents. |
| Decentralization. No single entity controls transactions and payments. | High volatility |
| No risk of inflation (for coins with limited emissions, such as Bitcoin) | Loss of a private key or seed phrase leads to the loss of funds because there is no way to restore the wallet without that information. |
| Security. Blockchain (as well as user wallet) can't be hacked if the private key or seed phrase hasn't been exposed. | Cryptocurrency mining difficulty is constantly increasing due to the increasing number of miners. This leads to losses from outdated, low-performing equipment. |
The high price volatility is one of the main drawbacks of cryptocurrencies and the primary reason for mistrust. What about the other disadvantages of digital currency, though? For example, regulation. Initially, BTC was a fully decentralized and independent currency. This means that the network member in the USA and the network member in Burkina Faso are equal. However, more and more countries are thinking about regulating cryptocurrencies. And in some parts of the world (Bolivia, Indonesia, Thailand) it is prohibited at the government level. The disadvantages also include reputation. Due to its anonymity, cryptocurrency has become a payment tool used in the black markets. A potential drawback is the "51% attack" threat when 51% of mining capacity or 51% of all coins (in the case of Ethereum) fall into the hands of one participant. Then this participant will completely control the blockchain and will be able to duplicate transactions. This is practically impossible because doing so doesn't make any financial sense cost-wise. See the illustration below to understand a "51% attack better".

Bitcoin's “51% attack” explained
In other words, no one will benefit from such an attack. Moreover, the more extensive the network, or the more users holding cryptocurrency, the more difficult it is to make the "51% attack".
Summary
Is there a future for cryptocurrencies? It is difficult to answer the question because everyone has their own definition of the word "future". Is the timeframe 10 years or 500 years from now?
However, the present is closely related to digital currencies. Since its introduction in 2009, the possibilities and popularity of cryptocurrencies are only growing. Therefore, we should expect intense crypto development in the first half of the 21st century.
Keep Exploring
Start exploring the world of cryptocurrencies by visiting the CoinMarketCap (CMC) website. It has a list of more than 2,500 cryptocurrencies with descriptions of their purpose and market metrics.
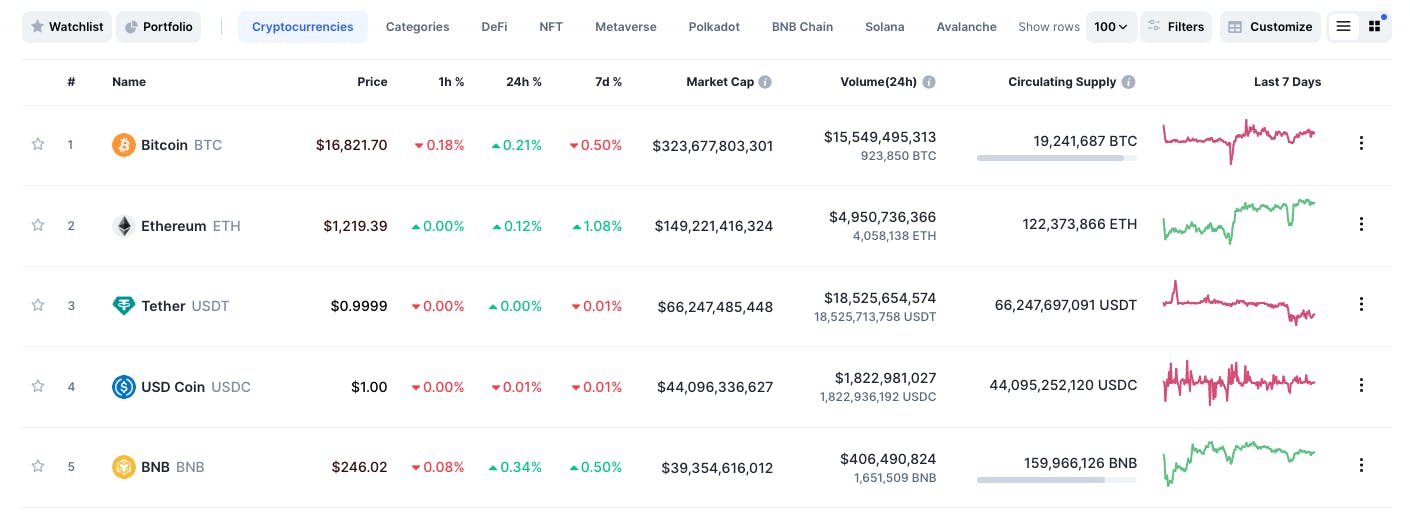
A quick overview of the columns on CMC and its meaning:
#: the list is sorted by market capitalization (Market Cap).
Name: the name of the cryptocurrency.
Price: the value of one unit (coin or token) at a given time.
Market Cap: Market capitalization refers to a cryptocurrency's total dollar market value. It is calculated by the following formula: Price x Circulating Supply. If there are 100 coins on the market with a price of $5, then the market cap is $500 (100 x $5).
Price: the current exchange price of the cryptocurrency.
Circulating supply: the number of coins on the market.
Volume (24h): number of coins traded on exchanges during a given day in a USD value.
Change (24h): change in price for the last 24 hours displayed in a percentage.
Price Graph (7d): visualized change in price for the last 7 days in the form of a chart.

