One of the best comparisons to Bitcoin is the Internet. The Internet has revolutionized how we use, share, and consume information. It made information decentralized, you don't have to go to the library every time you need to find something, and everything is currently online.
Money is also on the Internet now. We have online banking and debit/credit cards to use our digital money. The bottleneck within the current approach to money is the bank itself. Websites and mobile apps are just gateways to your bank account, and a bank is an intermediary that controls your account and money.
In contrast to banks and fiat currencies, Bitcoin gives its users complete control and full ownership of the account (wallet) and money (bitcoins). Your account doesn't need government insurance if it goes bankrupt, as any bank does. You, as a user, don't have any limitations on how you use your money. No matter who you are, where you come from, or how rich you are, everyone is equal and can benefit from all features.
Understanding Bitcoin
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin (abbreviated as BTC) is a digital payment system in which virtual "money" (bitcoins) circulates. Do you have a VISA or Mastercard plastic card? Both Visa and Mastercard are also electronic payment systems. However, they use our regular currency – dollars, euros, etc., and all transactions go through bank processing. Such currencies are called fiat. The Bitcoin system uses cryptocurrency – a purely digital currency that is not linked to any world bank or the economy of any country. It has its value, which is directly dependent on demand.
Let's compare three types of money and their traits: Bitcoin, Gold, and Fiat.

You can see Bitcoin outperforming gold and fiat money. As we advance, you will strengthen your knowledge about Bitcoin's traits and why it is setting new standards for how we use and understand money.
Critical features of Bitcoin. Why do we need it?

Permissionless. You don't have to ask anybody to use cryptocurrency. It's just a software that anybody can download for free. After you install it, you can receive and send Bitcoin or another cryptocurrency. You can even create your own currency. No one can prevent you. There is no gatekeeper.
The whole system is decentralized. No bank, agency, or government entity regulates Bitcoin. All network members are equal regardless of nationality or other characteristics. For example, in Visa and Mastercard, there are Gold, Platinum, or VIP cards. There are restrictions on the size of transactions that differ between members. But with Bitcoin, everyone is equal, and there are no limits.
Anonymity. When transferring the BTC, participants do not disclose their identities. For transactions, a bitcoin address (a hash with 27-34 characters) is used without disclosing other data about the recipient or sender. Remember the transfers between bank accounts or other electronic systems? Submitting a sender and receiver name, address, ID, and verified bank account number is required.
Irreversibility. All operations in Bitcoin are irreversible. They cannot be undone, stopped, or blocked. Theoretically, a complete rollback of the system (blockchain) is possible. Practically, it is impossible, being extremely difficult and costly to do.
Security. Bitcoin uses the SHA-256 encryption, so hacking a Bitcoin wallet is impossible. All data is stored in a particular file, access to which only you have. It is also impossible to "intercept" data during a transaction, as in the case of the banking system. Bitcoin uses cryptographic records – encrypted data that guarantees confidentiality and security. The only chance to steal your wallet data is if you don't store it securely - human factor (or social engineering), which has nothing to do with the Bitcoin network.
The direct nature of operations. In Bitcoin, transfers are made directly between participants – the P2P (peer-to-peer) principle is used. A transaction occurs without the participation of a third party like a bank, a processing center, or a server. Therefore, the operation in Bitcoin can't be tracked by anyone except its participants. By "can't be tracked", we mean that no one can influence or manipulate the transaction. Otherwise, all transactions are public, and anyone can go and check the record of every Bitcoin transaction, even the very first one.
History of Bitcoin Explained
The history of cryptocurrency has a vague chronology. For decades, cryptographers have worked to create a unique decentralized system, the work of which is based on mathematical calculations. Using their predecessors' experience and expertise, in 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto and Hal Finney created the world's first cryptography-based form of digital currency, or simply electronic money – Bitcoin. Nakamoto received the primary glory – they published a file with the Bitcoin protocol and briefly described the features of the new payment system. The smallest fractional part of the coin is named in his honor – 0.00000001 BTC, or simply one satoshi. In other words, one bitcoin is 100,000,000 Satoshi.

Why was bitcoin created? The reasons for the development of the field of cryptocurrencies are revealed by their features: anonymity, decentralization, security, and general accessibility. Ideally, the Bitcoin ecosystem should guarantee fast transactions without the participation of a third party (bank, payment processor, government) and with a high level of security.
An interesting point of view was expressed by the famous Russian businessman Sergey Mavrodi back in 2013:
"All this hype around cryptocurrencies is associated with its anonymity. People are tired of Big Brother watching their every action. Everyone is tired of this. And bitcoin, in this regard, is a breath of fresh air."
This quote answers the question of why bitcoins are needed. Transaction privacy is a crucial feature of cryptocurrencies.
How Bitcoin Works (for beginners)
The entire Bitcoin ecosystem rests on the blockchain. A blockchain is generally a time-stamped series of immutable data records managed by a cluster of computers not owned by any single entity. Each of these data blocks (i.e., a block) is secured and bound to each other using cryptographic principles (i.e., chain).
🤔 There should be a better way to explain this, right? Now, let's decipher it in simple words.
Imagine that each transfer (transaction) in Bitcoin is recorded on a separate page, a simple piece of paper (aka public ledger). The sequence of multiple pages forms the chapter of the book – a block.
To record a new page (conduct a new transaction), we need to "turn over" all the previous pages and chapters. This means that each new transaction is carried out in a chain – with the processing of old blocks (turning previous pages and chapters). A new book chapter can only begin after the old one is finished. And all the chapters form the book, and the blocks are the blockchain. Pages and chapters cannot be removed or edited. And access to the Bitcoin blockchain is open to all participants in the system.
Every participant (node/computer) has a copy of the book, which is always in sync with others. Suppose someone tries to change the information on previous pages, for example, to add illegal bitcoins to their wallet. In that case, other participants will notice that and compare it to copies of other participants. It will be rejected if the information doesn't match the previous records. This process happens automatically, and there is no need to do such checks manually.
Blockchain is an extensive open database in which encrypted information about all completed transactions is stored. As said before, every computer participating in the network has a full copy of the blockchain (book), constantly updating as new transactions and blocks appear.
Here are some other differences between "virtual" bitcoin and regular money:
- The form. Bitcoin is a currency that does not have a physical appearance. There are physical "paper wallets" with a QR code or wallets in the form of coins where BTC is stored. However, BTC cannot call them money in the truest sense. We can say that Bitcoin is a set of numbers generated by an algorithm. Not a paper note or a metal coin.

Value. The fiat currency exchange rate directly depends on the economic and political development of the country or confederation to which it is attached. Currencies in more than 100 countries are tied to the US dollar. The cost of bitcoin is determined by demand. It does not directly depend on economic processes (although it is indirectly linked).
Emission. Theoretically, fiat money does not have emission limits. They can be printed as many as Federal Reserve, or Central Bank wants. BTC has its own preprogrammed limit embedded in the system - 21 million coins (20,999,999, 9,769 coins, to be precise). According to forecasts, Bitcoin will reach this figure in the middle of the 22nd century. The only way of emission is mining, so the estimates are based on the mining difficulty and miner reward size. Difficulty increases or decreases with the number of competition among bitcoin miners. The more miners, the harder it is to mine new bitcoins. Miner reward size is a preprogrammed reward for the job they do, which is split in half every four years. Miner's reward is the only way to bitcoin emission. No one can change the size of the reward or issue more coins at will.

- Direct transactions. Even if we are talking about the electronic version of ordinary money (card, wallet), transactions are performed with the participation of a third party. In Bitcoin, the operation is direct (P2P).
BTC is more complex to evaluate than other common types of assets. Some features of bitcoin can be attributed to its advantages and its disadvantages. Let's take a look at the element of the irreversibility of transactions. On the one hand, you will receive the cryptocurrency you are sent – no system failure will block the transaction. On the other hand, this is a feature of Bitcoin that scammers or black market representatives exploit.
You might often hear that the speed of settlement of transactions is an advantage of Bitcoin. A transaction can take 10-20 minutes, sometimes an hour to settle. To complete it, you need 6 confirmations of other participants (nodes), which happen automatically. With a high network load of transactions, transfers settlement slows down because nodes need more time to confirm transactions. Another drawback is the regulatory activity of the authorities of different countries concerning cryptocurrencies. Formally, BTC creates the same conditions for all potential network participants. However, cryptocurrencies are banned in some countries (Vietnam, India, Ecuador, and partly China).
Some other disadvantages:
Unstable price: The potential of BTC as a payment option decreases due to high bitcoin's price volatility.
Fraud. Bitcoin itself is very secure and reliable. However, inexperienced people may fall for scam schemes: fake exchanges, fraudulent investment projects, viruses, social engineering, etc.
Where to Mine, Earn, or Buy Bitcoins
Like most other cryptocurrencies available, Bitcoin is generated through the use of the hardware power of computers (processors and video cards). This process is called Bitcoin mining. If in 2009-2010. To extract bitcoins, you could use a regular computer. To do so, you need powerful hardware rigs – mining farms. These farms combine dozens, sometimes hundreds, of video cards or particular processors such as ASIC miners. This wasn't always like that. In the early years of Bitcoin network development, you could mine tens and even hundreds of bitcoin on a regular home computer.

This equipment costs thousands of dollars and requires additional care and technical skills. For beginners, this method of obtaining BTC is not recommended. And in some countries, mining is wholly prohibited.
Here are other ways to get bitcoin:
Centralized Exchanges (CEX). There are dozens of online exchanges selling cryptocurrency for fiat. Most offer multiple currencies for sale, and if it is a cryptocurrency exchange, you will definitely be able to buy and sell bitcoin. Such exchanges have a simple and easy-to-use interface, similar to regular online stores. The most popular ones are Binance and Coinbase.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX). These are the platforms with more sophisticated interfaces primarily designed for crypto-crypto trading. However, they also offer purchasing of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies with a debit card or directly from a bank account. The most popular are dYdX and Uniswap.
Bitcoin faucets. These are services that distribute cryptocurrency to visitors for free. Hold on, though, don't run out right away to get free Bitcoin! There is nothing truly free in this world. You need to fill in the captcha or perform another task to get a small amount of BTC. There are hundreds of them online. The amount you can earn per task is tiny. I used one faucet and could receive only 0.00000027 BTC per hour, around $0.002.
BTM or Bitcoin ATM. You can buy Bitcoin through a specialized Bitcoin ATM by inserting cash into the machine. However, this method is the most expensive because BTM operators charge high fees, or the price is 7-10% above the market price.
What can be bought with bitcoin?
In cryptocurrency's early years, all transactions were conducted "informally". Buyers and sellers chatted in chat rooms (mIRC, Miranda), social networks, and forums. The most famous purchase of goods for bitcoin happened on the Internet forums. It is considered the first purchase of anything for cryptocurrency.
A user with the nickname Laszlo created a topic on the BitcoinTalk forum on May 18, 2010, titled "Pizza for bitcoins?". He asked who could order two pizzas for him for 10,000 BTC.
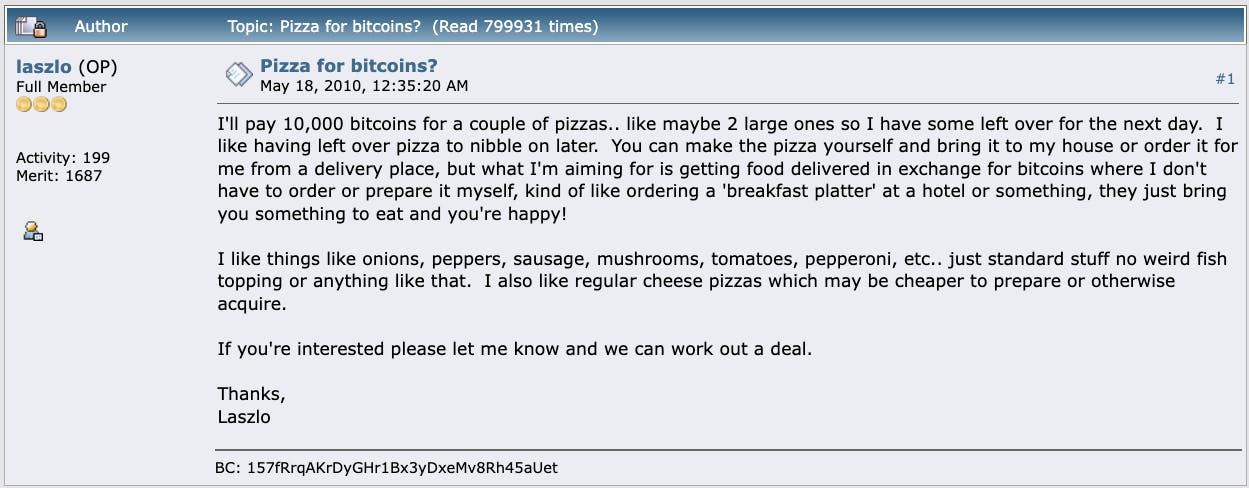
At the time, it was the equivalent of $30. One user agreed to the offer and ordered Laszlo a pizza, completing the first and most famous purchase using BTC.
Only a little time has passed since that moment, but BTC as a payment option has developed globally. In the summer of 2017, it became known that 260,000 retail stores in Japan would start to accept Bitcoin as payment. This is an essential step toward the globalization of payments in BTC. Nowadays, more and more car dealers, real estate agencies, jewelers, restaurants, bars, flight and hotel reservation platforms, and simple convenience stores are accepting Bitcoin as a payment option. It's hard to believe, but even some universities accept cryptocurrency payments for education.
Moreover, there are cryptocurrencies, like Dash, whose developers are creating an infrastructure for "unbanked" regions of our world. Their goal is to use and accept cryptocurrency as an everyday payment method for goods and services exchange. Every month, we read news about a new coffee shop, bar, or restaurant starting to accept cryptocurrency payments worldwide. In some countries, taxi drivers use bitcoin. In the United States, Republican Party supporters can donate money for its development in BTC. Cryptocurrency even got to space. Virgin Galactic, a space travel company, uses it.
Common crypto and blockchain myths
Crypto and blockchain are topics that have seen a lot of hype in recent years. However, there are still a lot of misconceptions out there about both crypto and blockchain.
❌ One of the most common myths is that crypto and blockchain are synonymous terms when they are separate technologies. Crypto refers to digital currencies such as Bitcoin, while blockchain is the technology behind them.
❌ Another common crypto and blockchain myth is that they are only used for illegal activities such as money laundering or drug trafficking. This simply isn’t true – crypto and blockchain are used for many legitimate purposes, such as banking and trading. Another myth is that cryptocurrency is completely anonymous when all transactions can be tracked on the public ledger.
❌ Finally, some believe blockchain technology is only useful for financial transactions when it has also been applied to other industries, such as healthcare and logistics. Although these myths can seem convincing at first, it’s important to remember that they are nothing more than misunderstandings of how crypto and blockchain work.
Summary
Bitcoin is the Internet of Money, developed by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008 and launched in 2009. It is a decentralized and anonymous platform for cheap and fast value transactions worldwide, available for everyone with computer or mobile device access. No registrations, qualifications, personal information, or proof of income is required to start benefiting from Bitcoin.
It is not backed by any type of asset or economy as fiat currencies are, so it is volatile. It is independent of external factors, gold mining volumes, a country's economic collapse, or poor monetary policy.
Bitcoin emission is limited to 21 million BTC, which will be reached in the 2100s.
The Bitcoin network has never been hacked or compromised since its very beginning.
This leads us to the conclusion that cryptocurrency is the most advanced payment system available now, one that can be used anywhere in the world and for any purpose, with literally no limitations. Anyone can make a payment gateway within minutes for any project. By anyone, I literally mean anyone, from the poorest and most undeveloped regions of the world up to the space station inhabitants. The only requirement to start accepting bitcoins to sell goods and services is a desktop or mobile device connected to the Internet. How cool is that?
Keep exploring
Head over to the Bitcoin page on CoinMarketCap and learn more about:
Price history (chart in the middle of the page)
Visit the blockchain explorer to see all bitcoin transactions and other interesting information in real-time such as:

